What are Black holes? know the formations, and classifications.
You might have heard about black holes present in the Universe. However, it was a myth and theoretical concept for many astronomers for centuries. Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity predicted the presence of black holes in the Universe in 1916. David Finkelstein for the first time explained a “black hole” as the region of space from which nothing can escape in 1958. However, the term “black hole” was coined in the year 1967 by American astronomer John Wheeler.
What is a black hole?:
“A black hole is an area of such immense gravity that nothing-not even light can escape from it,” says NASA. According to Wikipedia-” A black hole is a region of space-time where gravity is so strong that nothing-no particles or even electromagnetic radiation such as light can escape from it.” Now it can be defined that, a black hole is a cosmic or celestial body of very strong gravity, from which no matter even electromagnetic radiation can escape and it emits no light.
Astronomers and scientists believe that black holes are formed at the death of massive stars. When the fuels of the stars are exhausted, the binding energy of the stars disappears causing the collapse of the mass itself, which gives rise to a huge explosion and is compressed into a very small dark body compare to its original shape.
A black hole with a mass, ten times more than Sun, then its radius would be 30km or 18.6 miles, the astronomers say. A large black hole can have tens to millions of times the mass of the Sun, compressed to a very smaller one. Only the stars having more than three solar masses (one solar mass is equivalent to 1.989 x 1030 kilograms) become black holes at their death.
The circular like surface of the black hole is known as the “event horizon “and the center of the event horizon is called “singularity.” The radius of the event horizon is known as the Schwarzschild radius, after the German astronomer Karl Schwarzschild.
Schwarzschild in the year 1916, predicted the existence of collapsed stellar bodies, which did not emit light. The length of the Schwarzschild radius is proportional to the mass of the dead star. Every black hole has an accretion disk, a disk-like flow of gas, plasma, and dust particles around the event horizon, and a relativistic jet.(Stream of magnetized plasma produced by a black hole)

The black holes are unlikely to observe directly due to their smaller size and characteristics of not emitting radiation. However, they can be observed by the effect of their gravitational fields on nearby objects. When a solar mass comes within the purview of the gravitational field of a black hole, it runs so fast into the event horizon of the black hole that it radiates X-rays before disappearing forever. Black holes are ice-cold inside, but incredibly hot just outside.
The no-hair theorem:
The no-hair theorem first suggested by Jacob Bekenstein stated that, once a black hole becomes stable it can be observed with three properties including its mass, angular momentum, and electrical charge. The mass of a black hole can be assessed by Gauss’s law or Gauss’s flux theorem from far away.
Similarly, the angular momentum may be measured using frame dragging as predicted by the general theory of relativity from a very distant place. Like charge particle repeal the like charge particle, which is also applicable in case of a black hole. Wikipedia says “quantum field theory in curved space-time predicts that event horizon emits Hawking radiation with the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass”
Types of black holes:
On the basis of their nature and physical properties, scholars have classified black holes into four categories, such as stellar, nonstellar, supermassive, and intermediate-mass black holes.
Stellar black holes:
As discussed, only stars having more than three solar masses become black holes and emit no radiation coming under this type of black hole. German astronomer Karl Schwarzschild, in the year 1916 predicted the presence of collapsed stellar black holes in the Universe.
Center for Astrophysics, Harvard and Smithsonian source says-stellar mass black holes form from the collision of neutron stars. Astronomers have identified numerous stellar black holes in binary systems. Many black holes of such types have been identified in our home galaxy, the milky way and astronomers believe that hundreds of millions of solitary stellar black holes might have existed in our galaxy and emit no radiation.
Such types of black holes can be observed if a black hole is a member of binary solar systems. The black hole discovered in the year 1971, named Cygnus X-1, was a stellar black hole. NASA predicts the presence of a billion stellar black holes in the milky way.
The closest black hole to our earth named “The Unicorn”, ever discovered in the milky way is about 15,000 light years away from us. It is the smallest of black holes ever discovered which is about three times the mass of our Sun.
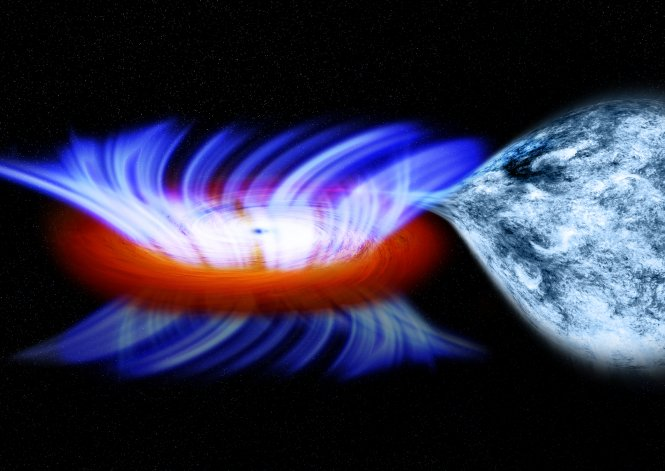

Nonstellar black holes:
Such types of black holes may exist in the galaxies in billions as suggested by Stephen Hawking, the British astrophysicist in 1971. Hawking’s theory suggests that uncountable primordial black holes with possible mass equal to or less than asteroids might have been created during the Big Bang, the period of origin of our Universe.
However, the mass of the nonstellar black holes must not be less than 10-8 kg to have escape velocity to exceed the velocity of light. These are also referred to as mini-black holes. They might be observed through particles that emit Hawking radiation.
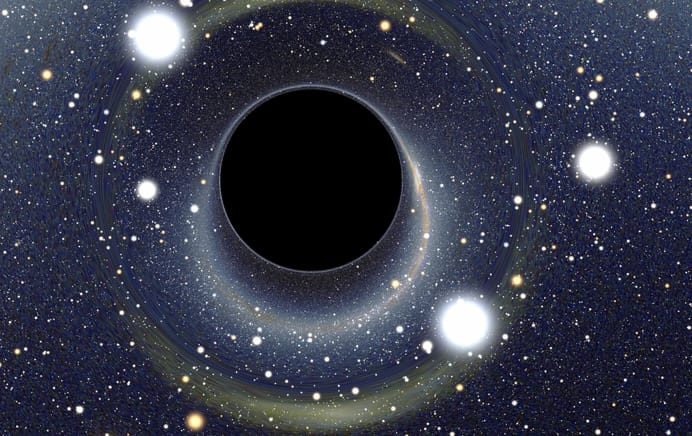

Supermassive black holes:
Supermassive black holes are killer black holes. After their formation, they grow massive by absorbing mass from surrounding stars and merging with other black holes. These black holes are bright enough to be detected from billions of light years away.
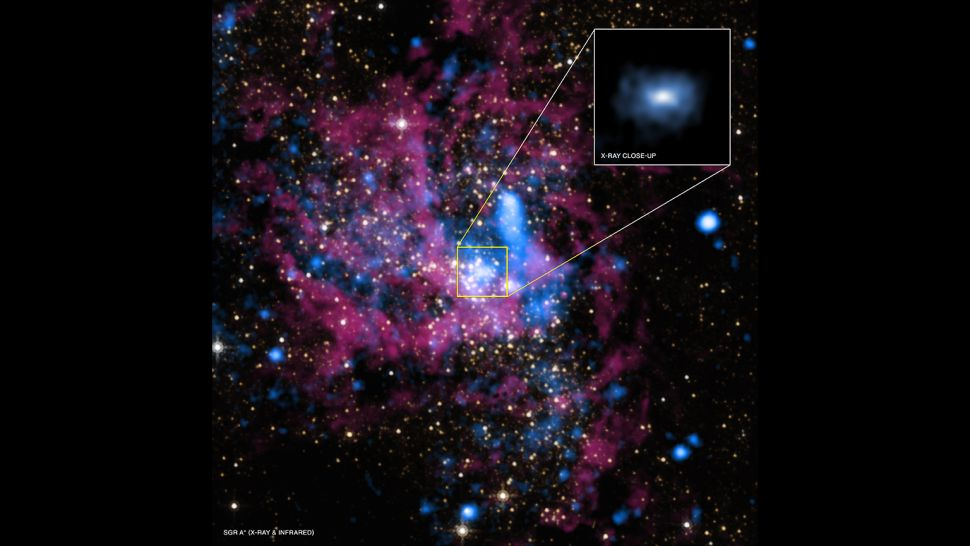
Most of astronomers and scientists believe that supermassive black holes exist at the center of most galaxies, and masses would be between 105-109 solar masses. The black hole identified as Sagittarius- A*, at the core of the Milky Way galaxy, is a supermassive one and its mass is about 4.3 million solar masses, which may be equivalent to masses of 4,000,000 Suns.
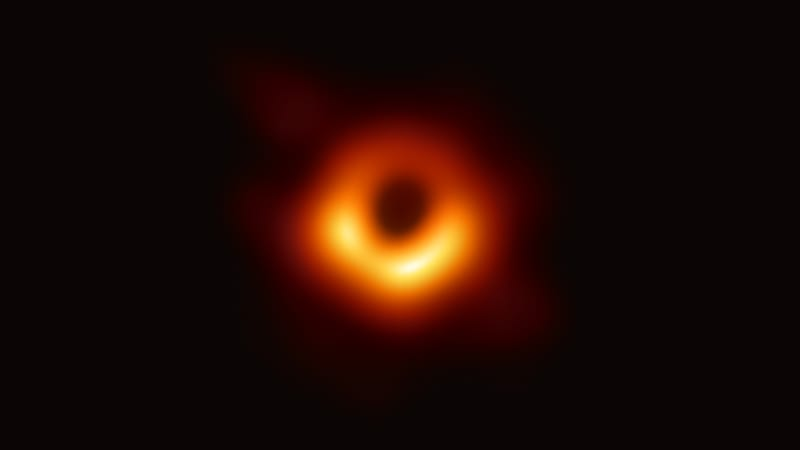

Intermediate-mass black holes:
The intermediate-mass black holes are still left mysterious to astronomers and researchers. The masses of these types of black holes may be in the range of 102-105 solar mass. The physical properties and their formation is still a mystery for astronomers.
Such types of black holes may be there in the Globular cluster Mayall- ll orbiting center of M31, the Andromeda galaxy, which is 18,000 times the mass of the Sun. One such type of first black hole GCIRS 13E was discovered by astronomers in 2004 in the milky way galaxy, where the mass of the black hole was assessed as 1300 solar mass.
In 2020 astronomers claimed to have possibly detected an intermediate-mass black hole, named 3XMMJ21522.4-055108 in the direction of the Aquarius constellation which is about 740 light years from earth.
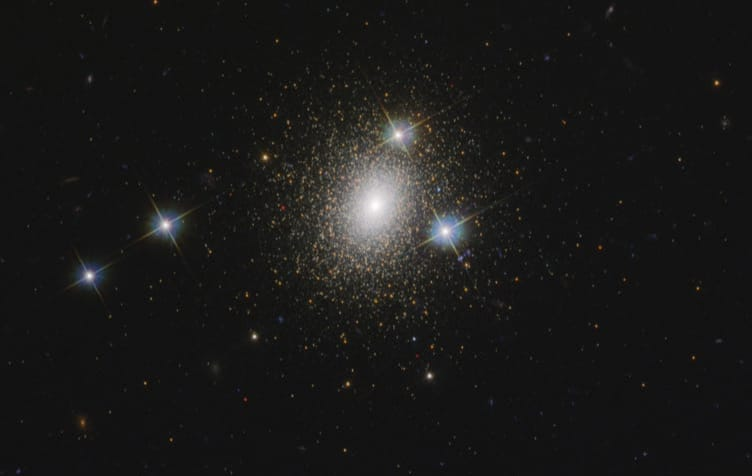

Image of Mayall ll or G1/ Image credit/ wikimedia.org
Bottom line:
Black holes are solar objects, created at the death of massive stars, where the gravity is so enormous that even electromagnetic radiation can’t escape. It is suspected that the core of the majority of galaxies has supermassive black holes. Astronomers and astrophysicists believe that our home galaxy milky way may be housed billions of black holes. The most common types of black holes are called stellar black holes. There is no threat from any black holes to our mother planet to date.



4 Comments
Stephen Hawking made Black hole papular in his Big Bang theory . Sir your description is very nice. Sir release these in a you tube channel
Thank you for suggestion, consider it in future
Universe is such a fascinating topic, it never leaves a chance to amaze you….. The more you explore the more you get….. it’s such a unexplored big mystery out there in the universe that can make our jaw drop……. Blackhole is among those…with the increase in research and technology we are now able to know about these valuable information that was unknown for years…… thanks for sharing information like this……✨💫👏👏
[…] Gamma Ray is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation with high frequencies and smallest wavelength and the highest energy. Gamma Rays are produced in nature by neutron stars, supernova explosions, lightning, and in the periphery of black holes. […]