The photovoltaic cell: it’s working and types of semiconductors materials.
A photovoltaic cell is an electronic device often referred to as a solar cell, composed of semiconductor materials that convert light energy into electricity directly. In a solar cell, the light may be reflected, absorbed or pass through the cell.
What is a photovoltaic cell?
A photovoltaic cell is an electronic device often referred to as a solar cell, composed of semiconductor materials that convert light energy into electricity directly. In a solar cell, the light may be reflected, absorbed or pass through the cell. A semiconductor is a material that can conduct electricity better than an insulator but not as good as conductors like metals.
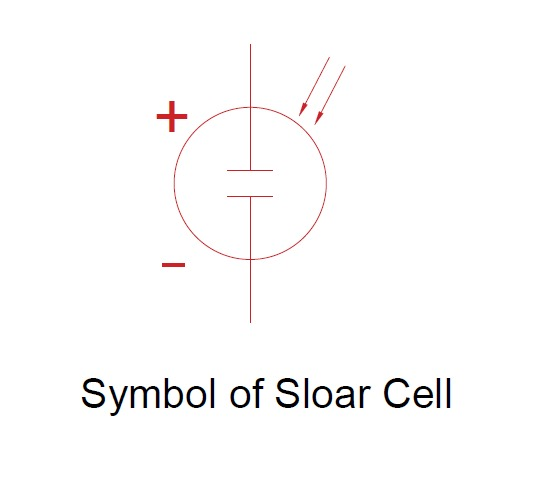
The amount of electricity produced from PV cells depends on different factors such as the availability of quality light( intensity and wavelength), multiple performances of the cell’s materials etc.( multiple semiconductor materials are used in the solar panels). A common silicon cell may produce about 0.5Volts, which may not meet the power requirement. To get the required amount of power multiple solar cells are integrated into groups in one plane called a solar panel or module. The modules are interconnected to form an array. An array is a power-generating unit, which may contain one or more modules.

Solar cells are typically connected in series to get the required voltage. However, they can be connected in parallel by electric lead to get a higher current. The preferred quantities of solar cells are 36 PCS or 40 PCS in one solar panel enabling the solar panel to produce approximately 16V, which can charge a battery having a rated voltage is 12 Volts. But the parallel connection needs better maintenance for its long efficiencies and productivity.
The solar panels have a sheet of glass facing the sun, allowing the light to pass and protect the semiconductors from corrosion, wind, hail stone and rain etc. Photovoltaic cells convert solar energy into DC electricity, whereas an inverter can convert DC power to alternating current (AC) power.
It is a very important factor regarding the photovoltaic cell is its band gap. The band gap is referred to as the energy difference between the top valence band and the bottom of the conduction band. It indicates which wavelength of light the material can absorb and directly convert to electrical energy. The band gap of silicon is 1.12eV(electron volt).
The working of photovoltaic cells:
A solar cell is made of semiconducting materials like silicon when exposed to sunlight, that absorb photons in the Sunlight. Photovoltaic cells have been fabricated into positive junction (p-junction) and negative junction(n-junction). Such junctions are created by doping one side of the device exposed to light with atoms of phosphorus(n) and another side doped with atoms of boron(p). Phosphorus has one more electron than silicon whereas boron has one lesser electron. An electric field is created at the p-n junction between the two layers of the device.
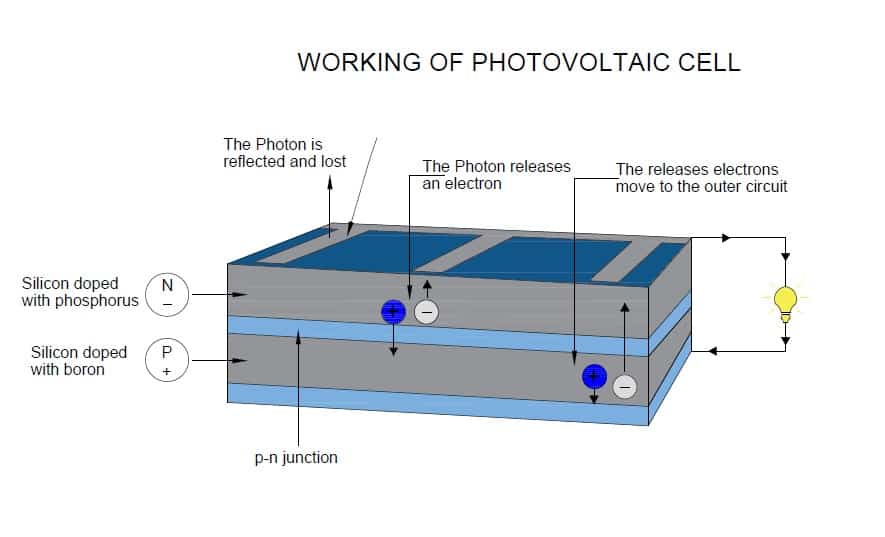
Photons are tiny elementary particles that comprise the wave of electromagnetic radiation. When the photons hit the semiconductor materials such as silicon, in solar panels, the negatively charged particle electrons are excited from the valance band to the conduction band, creating electron-hole pairs. When electron-hole pairs are created near the junction between positive and negative materials, the electrons are swept to the n- side( front side of the cells) by an electric field, causing excess holes on the p-side( back side of the cells)making a voltage potential like -ve and +ve terminals of a battery. The electrons and holes are connected by an external load to get electrical energy.
Types of semiconductor materials:
Solar cells are manufactured from a few types of semiconductor materials including the most commonly known materials silicon, and germanium.
Silicon:
Silicon is the most common semiconductor material used since 1950. It has four valence electrons and melts at a very high temperature of 1,414 degrees Celsius. Such material is being used for the production of solar cells including most of the common semiconductors used in computer chips. Silicon material is easily and plentily available on earth. It is used as a semiconductor material in about 95% of the total photovoltaic cells. Solar cells containing silicon semiconductors are highly efficient, reliable and cost-effective.
Germanium:
Germanium is used as one of the earliest semiconductor materials. It has four valence electrons. However the emergence of silicon as the king of semiconductor material, germanium has almost lost its ground to silicon. However, it is occasionally used as the bottom cell in a multifunction concentrator device, as it has a low band gap.
Conclusion:
A photovoltaic cell is an electronic device often referred to as a solar cell. It is composed of semiconductor materials that convert light energy including artificial light into electricity directly. Silicon is the most common semiconductor material used in a solar cell. Photovoltaic cells have been fabricated into p-junction and n-junction. Such junctions are created by doping one side of the device exposed to light with atoms of phosphorus(n) and another side doped with atoms of boron(p). An electric field is created at the p-n junction between the two layers of the device. Different types of photovoltaic cells are made for this purpose.
FAQs:
What is a p-n junction?
A p-n junction is referred to the boundary between two types of semiconductor material. In a typical photovoltaic cell, one side of the cell is doped with phosphorus, referred to as n-type or negative type and the other side is doped with boron, referred to as p-type or positive type.
What is a single-junction solar cell?
A solar cell having a single p-n junction is called a single-junction solar cell. The conventional solar cells used in solar power plants belong to this category. A single-junction solar cell has a maximum efficiency of 35%.
What is a multijunction solar cell?
The solar cell contains more than one p-n junction is referred to as a multijunction solar cell. Production of such cells is expensive and normally used in space explorations.
How do photovoltaic cells works?
When the light or photons hits the photovoltaic cells or solar panel, electrons are released from the atoms causing a flow of electricity.

6 Comments
Well described Sir
Thankyou
[…] to the boilers in the solar power plant for the production of power. It has advantages over Photovoltaic cells, as a parabolic trough is cost-effective and requires less area than PV […]
Nicely explained.. 👌👌.
Thankyou 👍
[…] Photovoltaic cells are devices which can convert sunlight to electricity directly. It only needs sunlight, not direct radiation or artificial light to generate electricity. However, the conversion efficiencies of the device depend on the types of Photovoltaic cells, the material used and the technology employed in the cells. […]